Human metapneumovirus, or HMPV, is a virus that attacks the respiratory system. It was first found in 2001 and is now known to cause many respiratory infections. People of all ages can get it, and it can cause symptoms from mild to severe.
In this article, we’ll dive into what HMPV is, how it spreads, and how to keep safe from it. Knowing about HMPV is key to stopping its spread and staying healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Human metapneumovirus is a type of virus that affects the respiratory system.
- It was first identified in 2001 and is a significant cause of respiratory infections.
- Human metapneumovirus can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe.
- Understanding what is human metapneumovirus is crucial to preventing its spread.
- Human metapneumovirus hmpv can affect people of all ages.
- Knowing human metapneumovirus what is it can help you take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones.
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a big cause of respiratory infections in all ages. To know what HMPV is, we need to look at its definition and how it’s classified. It belongs to the Pneumoviridae family and is a negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus. This info helps us understand how it works and how to fight it.
Understanding Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
What causes HMPV is complex, with many factors playing a role. It was first found in 2001 and has since become a major respiratory infection worldwide. The spread of HMPV varies by region and population, so knowing its history and current trends is key.
Definition and Classification
HMPV’s definition and classification come from its genetic makeup. It’s a single-stranded RNA virus, with a single strand of genetic material. This is important for figuring out how to treat it.
Historical Background
HMPV was first spotted in 2001 and has since been a big player in respiratory infections. Knowing its history helps us understand how it has spread.
Global Prevalence
The spread of HMPV changes by region and population. Knowing this helps us create better ways to prevent and treat it.
By learning about HMPV, we can find better ways to stop and treat it. This knowledge is vital for reducing HMPV worldwide and improving health.
Common Symptoms of HMPV Infection
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that can cause symptoms from mild to severe. Common symptoms include cough, runny nose, sore throat, and fever. These symptoms are similar to other respiratory viruses, making it hard to diagnose HMPV just by symptoms.
Some people ask, is human metapneumovirus a cold? While HMPV symptoms can seem like a cold, it’s a different virus. It can cause more severe symptoms, especially in young children and older adults. Symptoms of HMPV can be divided into two groups:
- Mild symptoms: cough, runny nose, sore throat, and fever
- Severe symptoms: pneumonia and bronchiolitis, especially in high-risk groups
If you or a loved one has severe symptoms or is at high risk, seek medical attention. Knowing the symptoms of human metapneumovirus is key for early diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, HMPV symptoms can vary from mild to severe. It’s important to know the common symptoms to seek medical help when needed. By understanding HMPV symptoms, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from this respiratory virus.
Common Symptoms of Human Metapneumovirus
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) can spread quickly in places like schools and hospitals. It’s important to know how it spreads, who’s at risk, and when it’s most active. If you’re wondering how do you get human metapneumovirus, it’s through touching someone who’s sick, touching contaminated surfaces, or breathing in droplets from coughs and sneezes.
The risk of catching it increases in winter. In these times, human metapneumovirus quarantine might be needed to stop it from spreading. Here are some important points to remember:
- Close contact with an infected person
- Contaminated surfaces and objects
- Respiratory droplets released through coughing and sneezing
Knowing these details helps you take steps to avoid getting sick. By understanding how it spreads, you can protect yourself and others from HMPV.
HMPV can spread fast, especially where air doesn’t circulate well. By washing your hands often and staying away from sick people, you can lower the chance of getting it. This helps stop the virus from spreading.
| Transmission Method | Risk Factor |
|---|---|
| Close contact | Higher risk in crowded areas |
| Contaminated surfaces | Higher risk in areas with poor hygiene |
| Respiratory droplets | Higher risk in areas with poor ventilation |
The Lifecycle of HMPV in Human Body
The time HMPV stays in the human body is key to understanding its impact. Studies show it can last from 7-10 days, sometimes up to 14. During this time, it multiplies in the lungs, causing inflammation and damage. For more details, check out the human metapneumovirus wiki.
Here are some important facts about HMPV’s lifecycle:
- The incubation period is usually 3-5 days.
- Symptoms can be mild or severe, including cough, fever, and shortness of breath.
- The virus can severely damage the lungs, leading to pneumonia and bronchiolitis.
Knowing how long HMPV lasts and its effects is vital for treatment and prevention. By learning about the virus, people can protect themselves and their families.
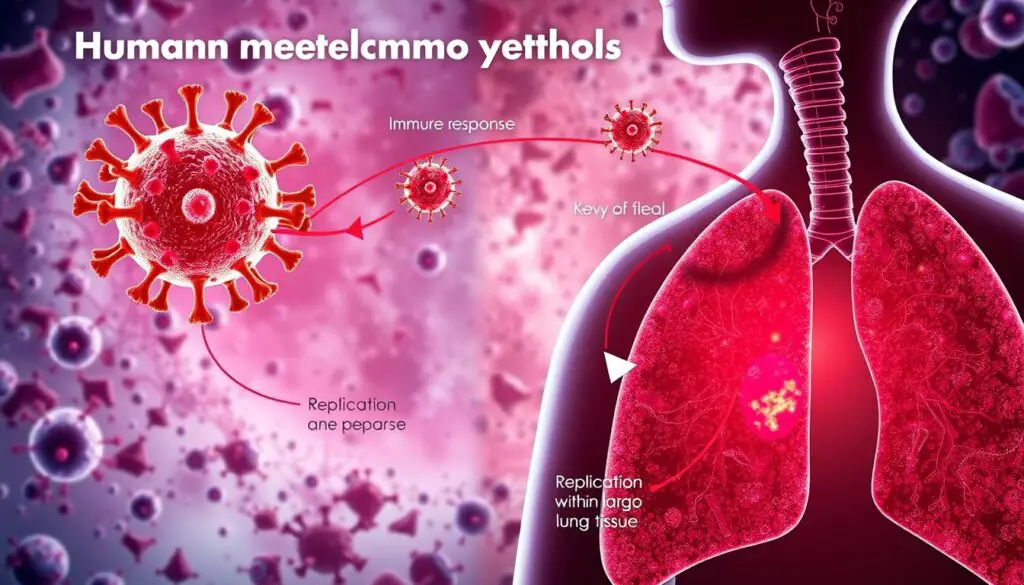
It’s crucial to rely on sources like the human metapneumovirus wiki for accurate information. Staying informed and proactive can help prevent infection and stop the virus’s spread.
| Day | Symptoms | Virus Replication |
|---|---|---|
| 3-5 | Incubation period | Virus begins to replicate |
| 5-7 | Mild symptoms appear | Virus continues to replicate |
| 7-10 | Symptoms peak | Virus reaches maximum replication |
| 10-14 | Symptoms subside | Virus begins to decline |
Diagnosing Human Metapneumovirus Infections
To find out if someone has human metapneumovirus, doctors follow a few steps. They look at symptoms, do lab tests, and might use imaging. This helps them find the right treatment and rule out other viruses.
Tests for HMPV include PCR, serology, and viral culture. To stay safe, wash your hands often and avoid sick people. Doctors also check for flu and RSV to make a diagnosis.
Testing Methods
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- Serology
- Viral culture
Differential Diagnosis
Doctors also check for other viruses like flu and RSV when diagnosing HMPV. Knowing the exact cause is key to treating the infection right and preventing it from spreading.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If symptoms like hard breathing or chest pain happen, get help right away. Learning about the virus and taking steps to prevent it can help avoid serious problems and improve treatment.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fever | A high temperature, usually above 100.4°F (38°C) |
| Cough | A dry or productive cough, which may be accompanied by wheezing or shortness of breath |
| Shortness of breath | Ddifficulty breathing or feeling winded, even when sitting still or engaging in light physical activity |
Treatment Options and Recovery
Human metapneumovirus treatment aims to ease symptoms and boost the immune system. Studies show that treating HMPV infections mainly involves managing symptoms like fever, cough, and shortness of breath.
Supporting the body’s recovery from human metapneumovirus can be done in several ways. These include:
- Rest and hydration to help the body recover
- Antiviral medications to alleviate symptoms
- Supportive care, such as nutrition and oxygen therapy, to help manage symptoms
It’s crucial to follow a healthcare professional’s advice for treating human metapneumovirus. They can offer tailored guidance and support. With the right treatment and care, most people can get better and go back to their usual activities.
Knowing about the treatment and recovery from human metapneumovirus infections helps manage symptoms. It also supports overall health and well-being.
Prevention Strategies Against HMPV
Preventing human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is key to stopping its spread. Good personal hygiene is a top way to avoid HMPV. This means washing your hands often with soap and water, especially after being near someone with the virus. Wearing masks can also help stop HMPV from spreading.
Keeping environments clean is another way to fight HMPV. This is very important in places like hospitals, where the virus can spread fast. Scientists are also working on a vaccine for HMPV. This vaccine would protect people from getting the virus.
Personal Hygiene Measures
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water
- Wear a mask when coming into contact with someone who has the virus
- Avoid close contact with anyone who has the virus
Environmental Controls
Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces can stop HMPV from spreading. This includes cleaning often-touched areas like doorknobs and light switches.
Vaccination Development Status
Even though there’s no HMPV vaccine yet, scientists are making progress. A vaccine would protect people from getting the virus and help stop its spread.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Groups
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) can affect anyone, but some groups are at higher risk. This includes children, babies, older adults, and those with weak immune systems. Studies show that human metapneumovirus in children and human metapneumovirus in elderly can cause worse symptoms and problems.
It’s crucial to watch these groups closely and seek medical help fast. This can help avoid serious issues and better their health. Here are some important points for each group:
- Children and infants: need close monitoring for signs of respiratory distress, such as wheezing or difficulty breathing.
- Elderly population: may experience more severe symptoms, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, due to weakened immune systems.
- Immunocompromised individuals: need aggressive treatment to prevent complications, such as secondary bacterial infections.
To lower the risk of human metapneumovirus in children and human metapneumovirus in elderly, we must take steps. This includes staying clean and getting vaccinated. By focusing on these groups, we can lessen the impact of HMPV infections.
| High-Risk Group | Special Considerations |
|---|---|
| Children and Infants | Close monitoring for respiratory distress |
| Elderly Population | Aggressive treatment for severe symptoms |
| Immunocompromised Individuals | Preventive measures, such as vaccination and good hygiene |
Long-term Health Implications
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infections can have big human metapneumovirus long-term effects on health. Studies show HMPV can cause breathing problems like asthma and COPD. These human metapneumovirus complications can really affect life quality and need ongoing medical care.
Some long-term health issues from HMPV infections include:
- Respiratory problems, such as wheezing and coughing
- Increased risk of developing asthma or COPD
- Recurring lung infections
It’s important to know about the human metapneumovirus long-term effects and prevent HMPV infections. Good hygiene and vaccines are key. By understanding human metapneumovirus complications, people can protect their health and well-being.

Conclusion: Living with HMPV Awareness
Understanding human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is key to stopping its spread. Knowing its symptoms and how it spreads helps us protect ourselves and our families. This knowledge lets us take action early to avoid getting sick.
HMPV affects many, especially kids, the elderly, and those with weak immune systems. By washing our hands often and keeping a safe distance from others, we help fight HMPV. These simple steps are crucial for keeping our communities healthy.
As scientists learn more about HMPV, we must stay alert and ready to act. By spreading the word about human metapneumovirus awareness and working with doctors, we can find better ways to treat and prevent HMPV. This will help those who get sick recover faster and more effectively.
FAQ
What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a virus that affects the lungs. It was found in 2001. It causes respiratory infections in people of all ages.
How does HMPV spread?
HMPV spreads through close contact and contaminated surfaces. It also spreads through respiratory droplets. The risk is higher in crowded places and during winter.
What are the common symptoms of HMPV infection?
Symptoms include cough, runny nose, sore throat, and fever. It can also cause pneumonia and bronchiolitis, especially in young children and older adults.
How long does the HMPV lifecycle last in the human body?
The HMPV lifecycle in humans lasts about 7-10 days. It can sometimes go from 3-14 days. This time, the virus harms the lung tissue.
How is HMPV diagnosed?
To diagnose HMPV, doctors use clinical evaluation, lab tests, and imaging. Tests include PCR, serology, and viral culture. It’s also compared to other respiratory viruses.
How is HMPV treated?
Treatment aims to ease symptoms and boost the immune system. It includes antiviral meds, antibiotics, and rest. Drinking plenty of water is also important.
How can HMPV infections be prevented?
Prevention involves good hygiene, controlling the environment, and vaccine research. There’s no vaccine yet, but scientists are working on it.
Who is at higher risk for severe HMPV infections?
Children, infants, the elderly, and those with weak immune systems are at risk. They need careful monitoring and strong treatment to avoid serious issues.
What are the long-term health implications of HMPV infections?
HMPV infections can cause respiratory problems like asthma and COPD. These can greatly affect life quality and need ongoing care.